The immunological assay that is commonly used in the medical industry to measure antigens, proteins, antibodies, and glycoproteins in laboratory samples is the enzyme known as Elisa Assay. When certain conditions are diagnosed, examples of which include pregnancy tests or HIV infections and cytokines measurement, for instance, these assays are generally used.
They allow for multiple samples to be conducted at one go inside of special absorbent plates also known as ‘Immuno plates.’ Each one measures a specific type of antigen and is widely available from pharmacies and medical institutions, as a kit.
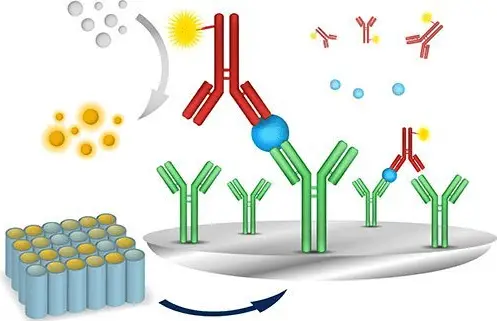
One of the main types is known as the ‘Sandwich Elisa’, as per the illustration shown in this source We look into this and other types in this article.
Sandwich ELISA – Steps in Laboratory Processes
When this method is used, two separate sets of antibodies are typically used. These can then detect any one of the products mentioned above such as Cytokines. There are a few steps in the process, as outlined below:
Step 1: The plate is coated with the antibody
Step 2: Any excess is then removed from the plate. The sample in question i.e. any secretion like urine or cell supernatant is added to the plate. This will then automatically bind to the concentration, and any excess removed.
Step 3: The antibody used to detect any inconsistencies is then added to the mix and either alkaline phosphatase or horseradish peroxidase is added. The samples are usually duplicated for statistical analysis.
Step 4: In the final stage a substrate such as ABTS or TMB is added which helps measure it more effectively in the reader. These help to determine the concentration of certain antigens which can then be calculated for density. A standard curve is then produced, as per the diagrams in this article: click here
Besides the method used above, there are 3 other types of ELISAs used, including the above-mentioned sandwich, plus, indirect, competitive, and direct, and each one has its benefits.
Direct
A sample or antigen that is immobilized directly onto the plate to aid the binding of the antibody to the protein is known as the direct method. only one antibody is used in this process and it is a less accurate means of finding out the amounts of analyte in any sample.
Indirect
Similar to its predecessor – the direct method, immobilize the plate, as well. However, it includes an additional step of detecting the protein.
After the first step which is to add a primary antibody to the substance, a secondary one is then added to detect any host species, this is the more specific resulting method when measuring endogenous antibodies in laboratories and other places.
Competitive

As one of the four types of ELISAs, the competition is the most commonly used one, and in instances where small molecules are a point of interest, and cannot be detected using any of the other types of Elisa assays instead of using an antibody, as per the above-mentioned methods, this one uses an antigen.
The more of it present in any samples (urine etc.), the less the antigen will stick to the antibodies. Here also substrates are used depending on the amount of protein in the sample.
These types of tests are highly sensitive and the reason behind this is because of the characteristics of the antibodies, which cause binding and amplification. However, the advantage is that the volume or number of samples used can be varied.
Other systems have also been implemented when detecting such substances and additional steps are also added by the use of various alkaline and polymers such as Streptavidin HPR and Phosphatase.
The 5 Basic Principles
There is also a basic principle(s) of the procedures that are used during this system to recognize or detect any biological specimen and these include the below 5:
1st Principle of Coating: a coating solution is typically implemented to bind any protein to the surface of the plate
2nd Principle of Blocking: blocking involves using a buffer so that any non-specific binding does not interfere with the process
3rd Principle of Detection Antibody: the protein usually always attaches itself to any analyte that is present in the sample
4th Principle of Substrate Addition: one the colored substrate is added, it acts as a catalyst for the enzyme
5th Principle of Analysis: it is always the case, then, after the above principles are applied, to analyze the data via an ELISA reader.
Various medical institutions use this method for a full range of applications including detecting specific antibodies in samples, glycoproteins, and soluble receptors in various serums amongst other uses, and one of the more recognizable uses has been over the past 2 years with lateral flows COVID-19 tests, to detect any viruses.
This technology has helped many medical facilities to treat various diseases as well and help to improve the accuracy of the detection of unfavorable substances in secretions.